
Alyssa Powell/Insider
- Net present value (NPV) is an economic measure that adds all potential outflows and inflows of an investment in today's dollars.
- A positive NPV means the investment is worthwhile; an NPV of 0 indicates the inflows and outflows are balanced; and a negative NPV means the investment is not desirable.
- To calculate NPV, subtract today's discounted value of all expected future returns from today's value of all expected investments.
- Visit Insider's Investing Reference library for more stories.
Net present value (NPV) is the product of the difference between an investment and all future cash flow from that investment in today's dollars. This provides businesses and investors with a way to determine whether to make an investment based on the current value of future returns.
NPV takes into account the time value of money, which says that money you have today is worth more than the same amount of money in the future. The declining value of future money is primarily due to inflation, interest rates, and the cost of lost investment opportunity,
Understanding NPV and how it's used
When you invest money, you want the return on your investment to exceed not only the amount invested but also make up for potential losses incurred due to the time value of money. NPV lets you convert future investment growth to today's dollars, giving you a more accurate picture of the true value of the investment.
Matthew Barbieri, CPA and commercial partner of Wiss & Company, cautions against using NPV as the sole deciding factor. "When investing in a startup, for example, you are investing in the team, the solution, business, model and execution," he says. "These are usually combined with a total addressable market to determine, in a broad way of speaking, 'Does the investment make sense?' If so, splitting hairs on a NPV calculation would be a waste of time."
NPV is used by businesses and investors in a variety of ways, including:
- To determine the viability of an investment or capital project. If the NPV of an investment is positive, meaning it's expected to make a profit, it's worth consideration. If it's neutral or negative, it should be rejected.
- To compare investment alternatives. When considering the NPV of several comparable investments, the one with the highest NPV should generally be undertaken.
- To guide capital budgeting. When a company is considering several major projects, NPV can be very helpful in determining the individual viability and value of each project.
- To evaluate potential mergers and acquisitions. Used in this way, NPV is paired with discounted cash flow (DCF), which is used to calculate the future value of the merger or acquisition.
NPV formula
When it comes to calculating NPV, the following formula shows how it is done.
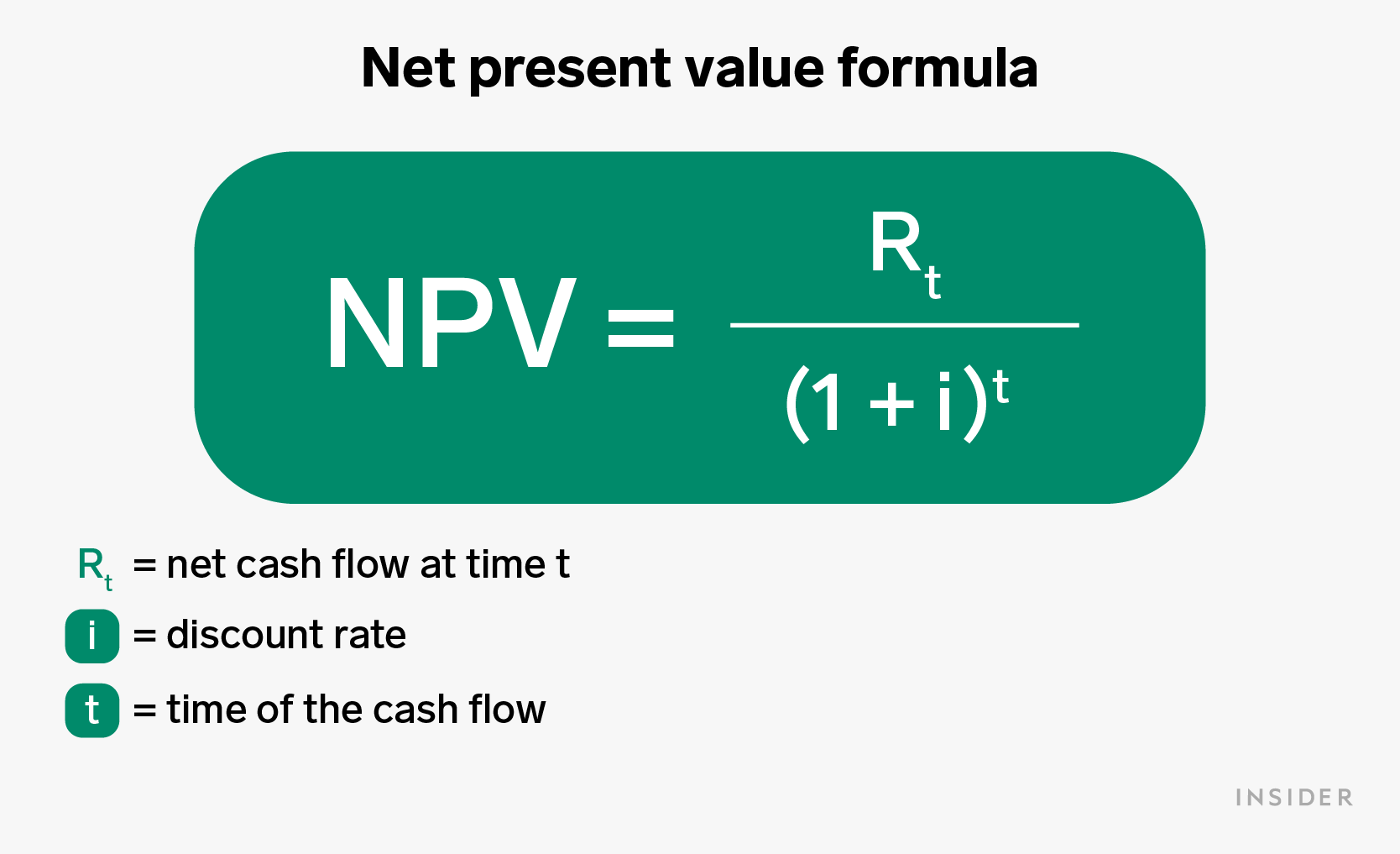
Alyssa Powell/Insider
NPV is the value (in today's dollars) of future net cash flow (R) by time period (t). To calculate NPV, start with the net cash flow (earnings) for a specific time period expressed as a dollar amount.
Divide that by the product of 1 plus the discount rate or interest rate (i) expressed as a decimal.
The discount rate can be the rate of return you expect to receive from this investment, the rate of return you could receive from an alternative investment, or the cost of the capital required to fund a project.
Is a higher or lower NPV better?
When NPV is positive, the investment is worth considering. When comparing similar investments, a higher NPV is better than a lower one. When comparing investments of different amounts or over different periods, the size of the NPV is less important since NPV is expressed as a dollar amount and the more you invest or the longer, the higher the NPV is likely to be.
A negative NPV indicates the investment will likely lose money and should not be undertaken. The same can be said for a neutral (0) NPV since your investment would not result in a gain.
The financial takeaway
Net present value provides a way for both investors and companies to compare potential investments or projects in today's dollars. Given the fact that the value of money decreases over time, NPV lets you compare financial "apples to apples," even when the comparisons are complex, to determine which investment is best.
Using the NPV spreadsheet function, comparisons are easy and quick. And while NPV is only one of many tools available to investors, it's a useful one and should be used in almost any investment decision.
